| Version 4 (modified by chunter, 7 years ago) (diff) |
|---|
802.11 Reference Design
- Download
- Changelog
- FAQ
- Architecture
Using the Design...
Benchmarks
- IFS Calibration
- Throughput
- Transmitter Characterization
- Receiver Characterization
- Pkt. Det. Min. Power Characterization
MAC
- PHY
Experiments Framework...
- Packet Flow
- FPGA Architecture
- FPGA Resource Usage
- App Notes
- Other Resources
- License
- Changelog
 | This page is under construction. Further details on how the 802.11 Reference Design realizes standard DTIM multicast buffering behavior will be published to this page soon. |
802.11 Reference Design: DTIM Multicast Buffering
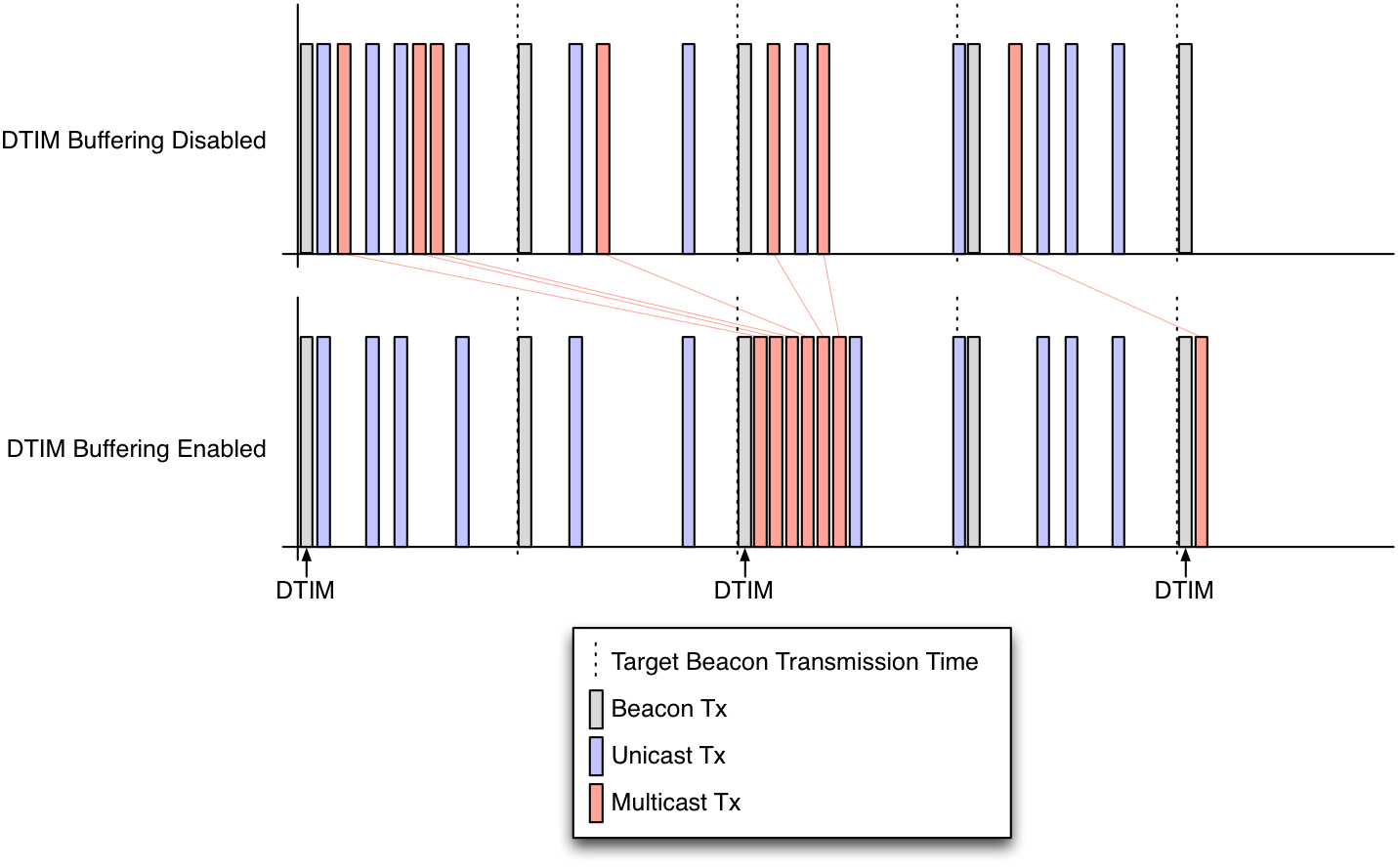
Many 802.11 client stations use a power savings mode in order to sleep when they are not actively transmitting or receiving. Part of the responsibility of an 802.11 AP is to defer multicast transmissions until a specified time when all client stations will wake from their power savings doze period in order to receive the traffic. The 802.11 standard specifies the time for multicast transmissions to be immediately following a beacon transmission that contains a Delivery Traffic Indication Message (DTIM).
The above diagram illustrates how the Mango 802.11 Reference Design schedules its transmissions to abide by the 802.11 standard when DTIM multicast buffering is enabled. After a DTIM beacon, all unicast traffic is suspended while the AP is able to dequeue all buffered multicast packets in a burst. Unicast transmissions resume as normal after the final multicast packet is transmitted. Note: a beacon and multicast burst can occur in between retransmissions of a unicast packet.
Attachments (1)
- DTIM_timeline.png (80.6 KB) - added by chunter 7 years ago.
Download all attachments as: .zip